
Published on the 4th August 2023 by ANSTO Staff
The release of the Oppenheimer film, the story of the director of the Manhattan Project, has prompted many people to go online and search for an explanation of the difference between fission and fusion, two fundamental scientific concepts.
Nuclear fission
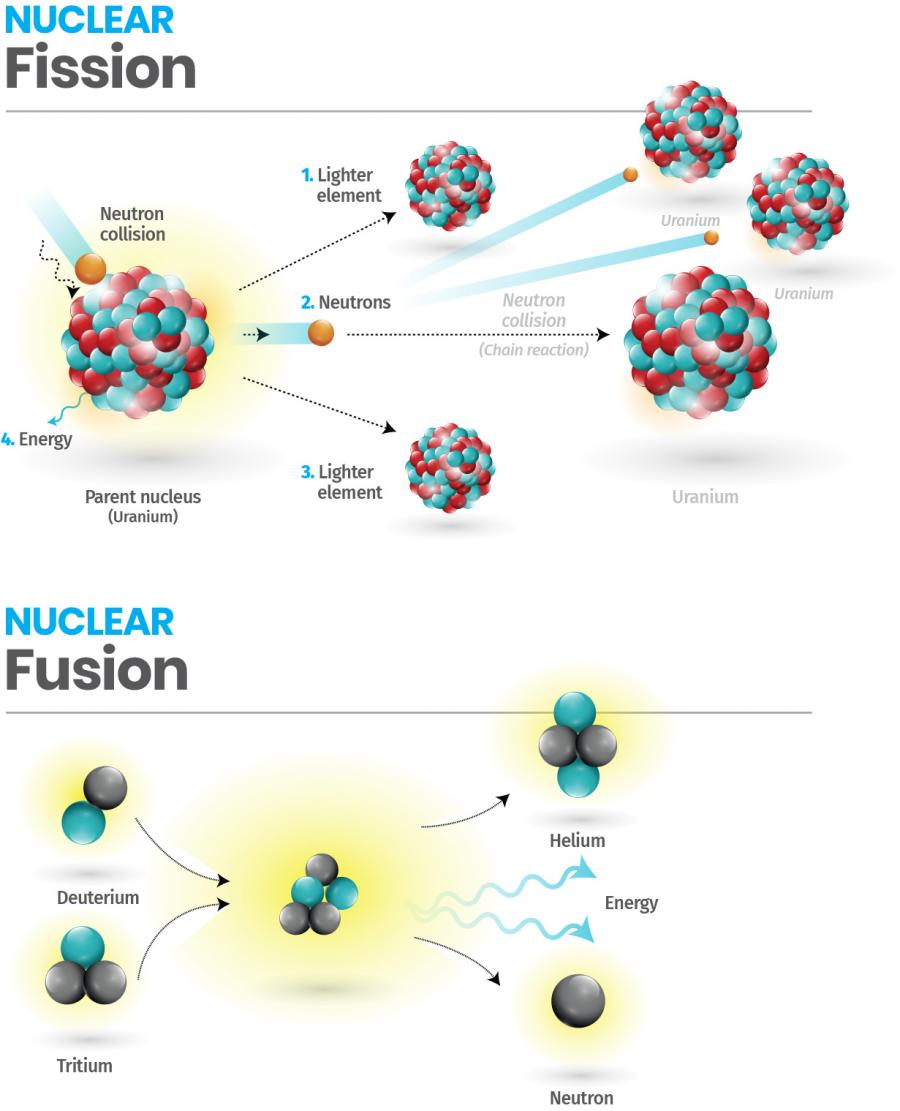
Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei and releases energy.
For instance, when hit by a neutron, the nucleus of an atom of uranium-235 splits into two smaller nuclei, for example, a barium nucleus and a krypton nucleus and two or three neutrons. These extra neutrons will hit other surrounding uranium-235 atoms, which will also split and generate additional neutrons in a multiplying effect generating a chain reaction in a fraction of a second.
Each time the reaction occurs, there is a release of energy in the form of heat and radiation.
Inside a nuclear reactor, such as OPAL, uranium atoms are split apart in a controlled chain reaction to release heat and neutrons.

Nuclear fusion
Nuclear fusion is the process by which two light atomic nuclei combine to form a single heavier one while releasing massive amounts of energy.
Fusion reactions take place in a state of matter called plasma — a hot, charged gas made of positive ions and free-moving electrons with unique properties distinct from solids, liquids or gases.
The Sun, along with all other stars, is powered by this reaction.
Ever since the theory of nuclear fusion was understood in the 1930s, scientists — and increasingly also engineers — have been on a quest to recreate and harness it. That is because if nuclear fusion can be replicated on Earth at an industrial scale, it could provide virtually limitless clean, safe, and affordable energy to meet the world’s demand.
It is easier to induce fission than fusion but there are numerous fusion energy projects around the world making progress, including the JET project in the UK, LLNL's National Ignition Facility (NIF) in the US and ITER.
ANSTO is the home of Australia’s nuclear expertise.
Content in this article was sourced from the IAEA. Read more:
https://www.iaea.org/newscenter/news/what-is-nuclear-fusion
https://www.iaea.org/newscenter/news/what-is-nuclear-energy-the-science-of-nuclear-power
Read the reviews of Oppenheimer by our scientists in Part 1 and Part 2.